
Name
1. Which choice is an acceptable Lewis structure for XeOF2 ? Lone pairs on terminal atoms not shown; assume all terminal atoms have octets. Structure d.
2. The diagram that best represents the molecular stereochemistry of XeOF2 is structure d.


3. Which compound is expected to be most ionic?
a) BeH2
b) TiCl4
c) MgF2
d) NF3
e) B2O3
4. Which cation produces the most acidic solution when its chloride is contacted with water?
a) Mo6+
b) Ru3+
c) Mg2+
d) Fe3+
e) S4+
5. Which species is most likely to occur in the lower left corner of the Pourbaix diagram for ruthenium?
a) RuO4
b) Ru(OH)2
c) Ru3+
d) RuO2
e) Ru(s)
Questions 6-10 concern the following redox half reactions and their corresponding standard reduction potentials
a) Cl2(g) + 2e ® 2Cl-(aq) e 0 = 1.36 V
b) Ca2+(aq) + 2e ® Ca(s) e 0 = -2.76 V
c) H2SO3(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 4e ® S(s) + 3H2O e0 = 0.45 V
d) Co2+(aq) + 2e ® Co(s) e 0 = -0.28 V
e) Ru3+(aq) + 2e ® Ru2+(aq) e 0 = -0.084V
6. The half reaction that is most spontaneous as written under standard conditions is a.
7. The strongest oxidant (oxidizing agent) is in reaction a.
8. The strongest reductant (reducing agent) is in reaction b.
9. The half reaction whose reduction potential depends on pH is c.
10. The reaction(s) that could be used to oxidize H2(g) is (are) a,c.
11. The first few pKa values for H3AsO4 are 2.8, 7.3, and 11.8. Which species will predominate in an aqueous solution having pH = 6.5?
a) H3AsO4
b) H2AsO4-
c) HAsO42-
d) AsO43-
e) H4AsO4+
12. Which substance has the highest total covalent bond energy?
a) H2O
b) H2S
c) CO2
d) SO2
e) OF2
13. Which fundamental property of the atom is primarily responsible for the fact that the first electron affinity tends to increase left to right in a period of the Periodic Table?
a) Electronegativity
b) Effective nuclear charge
c) Enthalpy of atomization
d) Atomic number
e) Principal quantum number of the valence shell
14. Which substance is unlikely to function as a Lewis acid?
a) SO2
b) SnCl2
c) (C2H5)2O
d) SiCl4
e) C2H4
15. The stereochemistry of PF4- is best described as
a) tetrahedral
b) square planar
c) trigonal planar
d) see-saw
e) T
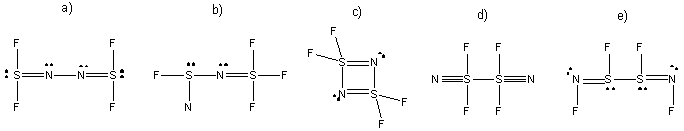
16. Which structure(s) for S2N2F4 is (are) reasonable in terms of expected bonding patterns for S, N, and F? Lone pairs on terminal atoms are not shown--assume an octet for each terminal atom. a,d, and e.
17. Which compound produces a basic solution when added to water?
a) NaF
b) SO(OH)2
c) VCl3
d) TiO2
e) SnCl2
18. Reaction of the Lewis acid, SnCl2, with the Lewis base, F-, gives the adduct, SnCl2F-. Which statement is true?
a) Hybridization at Sn does not change.
b) Hybridization at Sn changes from sp to sp2.
c) Hybridization at Sn changes from sp2 to sp3.
d) Hybridization at Sn changes from sp3 to sp3d.
e) Hybridization at F- changes from sp3d to sp3d2.
19. How many reasonable resonance forms can be drawn for HClO3?
a) one
b) three
c) four
d) seven
e) nine
20. Which Lewis acid is expected to have the greatest affinity for the Lewis base, SH-?
a) H+
b) SO3
c) BF3
d) Sn4+
e) Pb2+
21. Which substance is expected to be insoluble in water?
a) K2CO3
b) KOH
c) K3PO4
d) KClO4
e) KC2H3O2
22. Which cation is expected to have the largest Z2/r?
a) U6+
b) S6+
c) Fe6+
d) Mo6+
e) Te6+
23. The enthalpy change for the reaction
2Ag+(aq) + Cu(s) ® 2Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq)
is approximately
a) -300 kJ
b) -150 kJ
c) 0 kJ
d) 150 kJ
e) 300 kJ
24. The lattice energy for an ionic solid with formula, M2X3, is about -12000 kJ/mole. The lattice energy for the compound, MY3 (where M is the same cation), is then expected to be ABOUT
a) -800 kJ/mole
b) -3200 kJ/mole
c) -4800 kJ/mole
d) -6400 kJ/mole
e) -9600 kJ/mole
25. Which species would be predicted by VSEPR to have see-saw stereochemistry?
a) CF4
b) SeF4
c) ClF4-
d) BF4-
e) PF4+