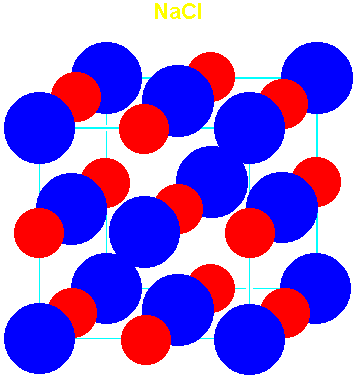
(NaCl)
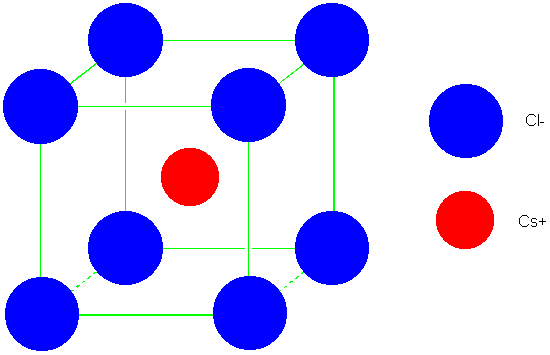
(CsCl)
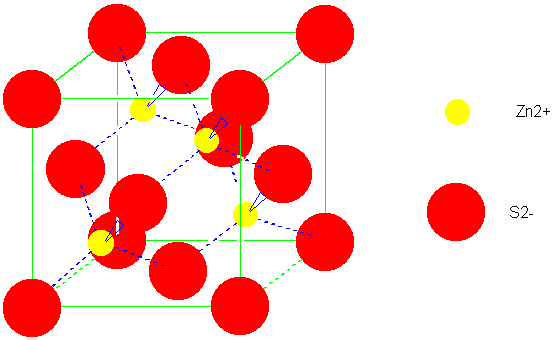
(ZnS)
CaF2

| Radius Ratio
(Cation/Anion) |
Lattice Type | CN of Cation | CN of Anion | Madelung
Constant |
Reduced
Madelung Constant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. 1:1 Stoichiometry of Salt(MX) | |||||
| 0.225-0.414 | Wurtzite(ZnS)
Zinc Blende (ZnS) |
4 | 4 | 1.63805 | 1.63805 |
| 0.414-0.732 | Rock salt (NaCl) | 6 | 6 | 1.74756 | 1.74756 |
| 0.732-1.000 | CsCl | 8 | 8 | 1.76167 | 1.76267 |
| B. 1:2 Stoichiometry of Salt (MX2) | |||||
| 0.225-0.414 | Beta-quartz (SiO2) | 4 | 2 | 2.201 | 1.467 |
| 0.414-0.732 | Rutile (TiO2) | 6 | 3 | 2.408* | 1.605 |
| 0.732-1.000 | Fluorite (CaF2) | 8 | 4 | 2.51939 | 1.6796 |
| C. 2:3 Stoichiometry of Salt (M2X3) | |||||
| 0.414-0.732 | Corundum (Al2O3) | 6 | 4 | 4.1719* | 1.6688 |
| Born Exponent | Principal Quantum Number
of Outermose Electrons of Ion |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | H-, Li+ |
| 7 | 3 | F-, Na+ |
| 9 | 3 | Cl-, K+, Zn2+, Ga3+ |
| 10 | 4 | Br-, Rb+,Cd2+, In3+ |
| 12 | 5 | I-, Cs+, Au+, Tl3+ |
| Lattice Name | Lattice Structure |
|---|---|
| Rock Salt
(NaCl) |
 |
| Cesium Chloride
(CsCl) |
 |
| Zincblende
(ZnS) |
 |
| Fluorite
CaF2 |
 |
Examples:
All alkali halides except CsCl, CsBr, CsI
AgCl, AgBr, AgI
Most of M2+ oxides
Alkaline earth monosulfides except BeS.
Many transition metal sulfides
CaC2--has Ca2+ at Na+ positions, C22-
at Cl- positions along Ca-Ca axis.
NH4Cl (> 184o), NH4Br (> 138o),
NH4I (> -17.6o)
TlF (deformed)
Example:
CsCl, CsBr, CsI, CsCN, CsSH
TlCl, TlBr, TlI, TlCN
Be(H2O)42+SO42-
K+SbF6-
NH4Cl (< 184o), NH4Br (< 138o),
NH4I (< -17.6o)
Example:
BeS, ZnS, CdS, HgS, AgI, CuCl, CuBr, CuI, BN, BP
Example:
ZnS, CdS, HgS, NH4F
Example:
Transition metal sulfides, arsenides, selenides.
Example:
TiH2, CaF2, SrF2, BaF2,
CdF2, HgF2, PbF2, SrCl2, EuF2
Related is the antifluorite lattice (M2X), w anion/cation roles reversed.
Example:
Li+, Na+, K+ oxides, sulfides, selenides, tellurides. Mg2Si
and other group II-group IV cpds.
Example:
Metal difluorides and dioxides, but not sulfides or other dihalides.
Lattice seems to be appropriate for highly ionic cpds.
Difluorides of Mg, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pd; CaCl2;
CaBr2;SrCl2
------anions------
------cations----- repeats
------anions------ >BR>
# formula units/uc = 2
Requires considerable covalence in cation-anion interaction.
A cations in 1/8 of Td sites (equiv to Ca2+ positions
in CaF2).
B cations in 1/2 of Oh holes, with alternating rows (not
layers) missing.
# formula units/uc = 2
# O2- = 1/8 (8) + 1/2 (10) + 1/4 (4) + 1 = 8
# A = 2
# B = 1/4 (8) + 1/2 (2) + 1 = 4
C.N.'s O2- = 4 (÷Td) (3B and 1A)
A = 4 (Td)
B = 6 (Oh)
Example:
MgAl2O4 (A2+B23+O4)
Sum of cation charges = 8
Na2WO4 (A6+B2+O4)
Zn2SnO4 (A4+B22+O4)
NiAl2O4 (A2+B23+O4)
Inverse Spinels-- A and half the B trade places, so we have A in Oh holes, half the B in Oh and half in Td holes.
In these cases, A is transition metal which would be HS in Td
hole, LS in Oh hole.
Example:
Fe3O4 (Fe2+Fe23+O4)
NiFe2O4
CoFe2O4
NiGa2O4
Example: BaTiO3